The human body naturally produces growth factor hormones all your life, but the levels will change depending on your age and lifestyle. The levels of insulin-like growth factor 1, responsible for promoting energy, a robust immune system, enhanced fat burning, stronger bones, youthful looking skin, speed up healing, repair muscle tissue, and athletic physique, peak around your early 20s and start to decline around middle age rapidly. This is the reason, so many middle-aged people begin looking for anti-aging supplements—they feel much older than they actually are.
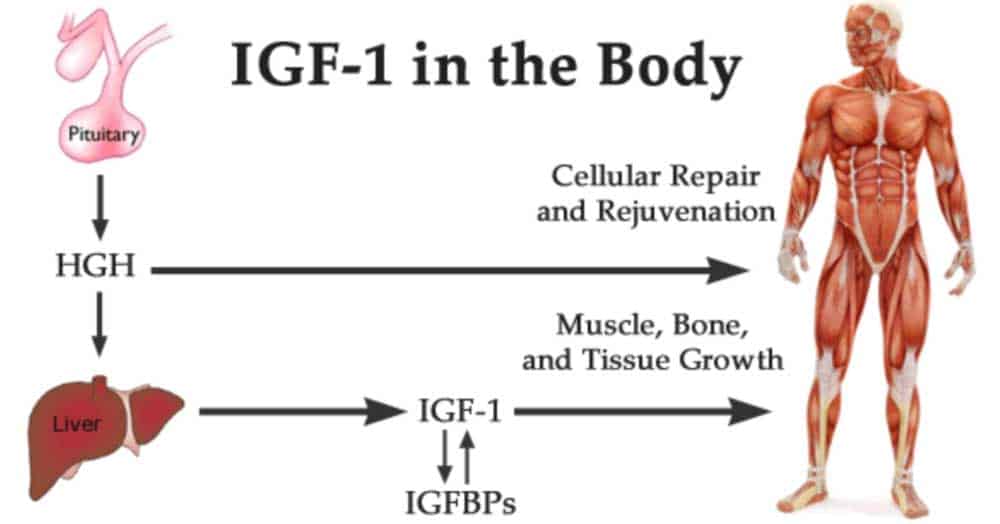
IGF-1 is part of an ancient signaling system that promotes growth in many species. The system includes insulin, a protein structurally very similar to IGF-1 (hence the name). Insulin is a mediator of lifespan regulation through food, exercise, and the energy metabolism. Some proteins carry instructions in the blood; they attach to receptors on the surface of a cell and tell the cell what to do. Others get inside the cell and play a more direct role in the chemistry. IGF-1 does both. It has “both endocrine and autocrine functions.”
Below is an excellent example of how we have way more of both growth hormone and IGF when we are growing children than later in life.

Human Growthh Hormone / HGH

Why is IGF-1 Better Than HGH
IGF-1 offers all of the same benefits as HGH, without any of the harmful effects. First, let us explain how the medication works.
The real difference between the two ingredients becomes apparent when you begin administering them. When you inject natural IGF-1, your body will replenish its levels to their optimal amount, and then filter out the excess through the kidneys. All a while, your body will still be producing its own insulin-like growth factor 1. However, when you inject with HGH, your body will actually stop producing the hormone, causing the medication to do the opposite of what they were intended to do.

